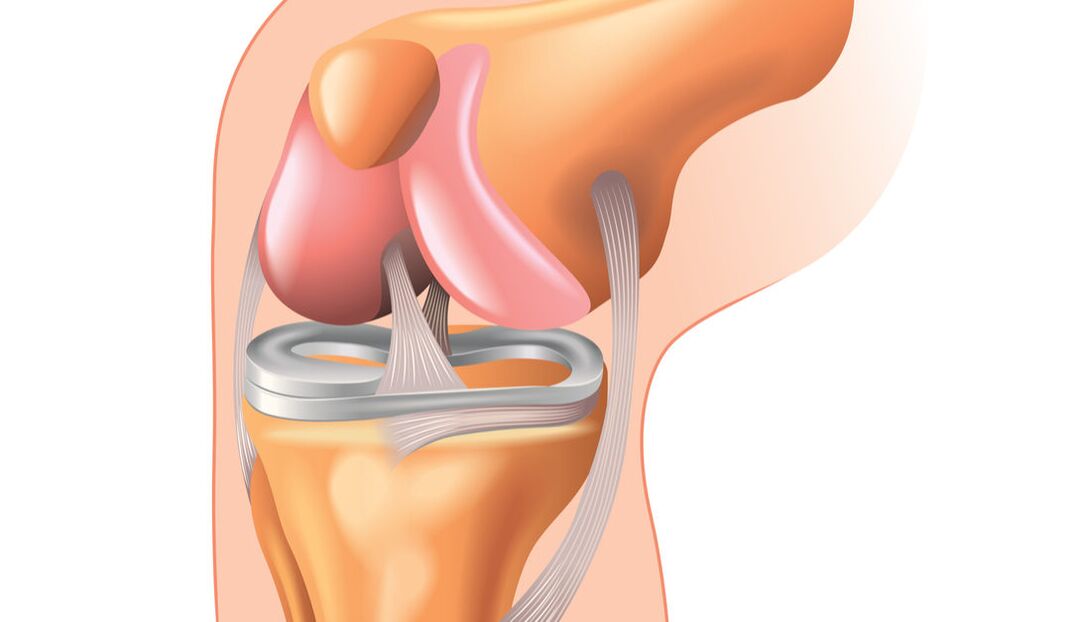
What is joint disease
disease cause
- congenital joint pathology;
- Dysplasia;
- Injury, surgery;
- Removal of the meniscus or part of it;
- arthritis;
- Lumbar spine disease;
- hormone imbalance;
- Low metabolism.
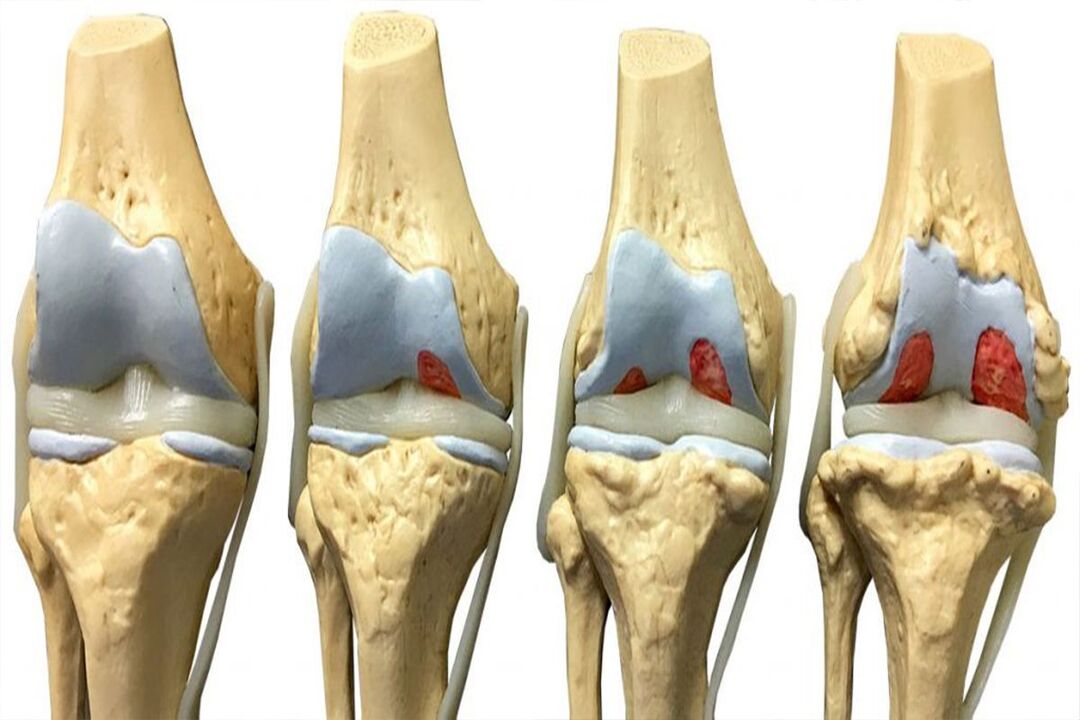
Stages and symptoms
- There are no obvious clinical symptoms at this stage. Mild discomfort and pain may occur after prolonged exercise, which will disappear after rest. You will feel pain when you get up in the morning and move around, but it will disappear after a while. Grade 1 arthropathy is rarely diagnosed incidentally during routine examination.
- Increased knee pain and stiffness. One saves one's legs and tries to lighten their load. As a result, muscles atrophy, joint deformations can be felt, and the legs at the knees cannot fully extend.
- The pain is constant. The legs do not straighten or bend, making it difficult to walk. Partial or complete loss of mobility. The cartilage is completely destroyed, and friction between the bones of the joint increases with the formation of osteophytes.
diagnosis
- General and biochemical blood tests;
- rheumatism test;
- radiography;
- Ultrasound and MRI can detect disease at an early stage;
- Arthroscopy.
Treatment of knee joint disease
Complications and prevention
- joint deformity;
- Cosmetic defects - curvature of limbs;
- Infections of the blood or lymph fluid from other sources in the body;
- Because the ligaments are weak, dislocations and fractures can occur even during normal walking;
- Bone fusion (ankylosis) occurs in the joint area, resulting in loss of movement.